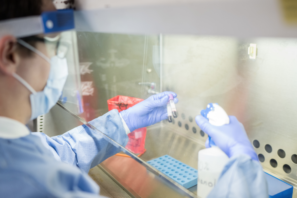
UF Health researcher Barry Byrne, M.D., Ph.D. is working to develop a COVID-19 vaccine.
UF Psychiatry Professor Carol Mathews writes for The Conversation.
Telemedicine became standard practice, even though it was rarely used before the pandemic.
University of Florida Health has enrolled its first patient in a clinical trial for the Regeneron Pharmaceuticals’ monoclonal antibody cocktail to treat COVID-19.
Cindy Prins, Ph.D., offers infection control assessments for UF entities who aim to resume activities throughout campus.
NIH has launched two adaptive clinical trials evaluating the safety and effectiveness of blood thinners to treat COVID-19.
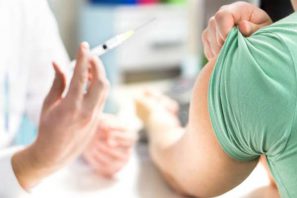
A Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine is administered to the first group of frontline healthcare workers at UF Health Jacksonville.
For many of us, the COVID-19 pandemic has brought plenty of novelty to our lives, like wearing masks and physical distancing. One aspect, though, gave financial economists déjà vu, and it’s looking a lot like 2008.
John Smulian, chair of the UF College of Medicine’s department of obstetrics and gynecology, provides important information on what is known about the novel coronavirus and pregnancy.
While many spots on campus sit empty, the Department of Physics’ Machine Shop is up and running to aid in an important effort to protect health care workers.
It’s a term we’re going to hear much more frequently during the final chapter of the COVID-19 pandemic — herd immunity.
A UF team of infectious disease experts propose a core protocol for such vaccination trials.