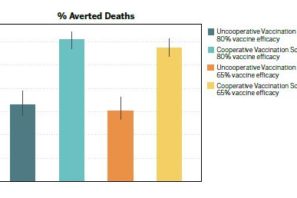
Which global distribution strategy for a hypothetical COVID-19 vaccine will save the most lives?
Many Americans are simply touching their faces too often during the novel coronavirus pandemic, public health officials have observed, potentially increasing their exposure to the pathogen.
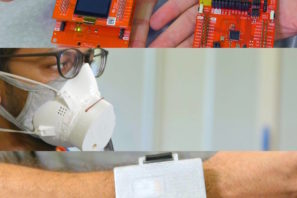
A wristband that tells kids when they’re too close together at school. A wearable that detects a possible COVID infection before you feel sick.
UF researchers sifted through several thousand studies on human coronaviruses related to the novel SARS-CoV-2 which causes COVID-19, with the goal of learning from the past to help shape the future.
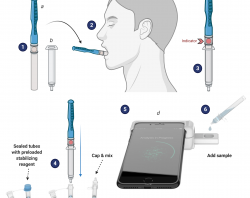
A UF professor won 2nd place in a technology competition sponsored by the NIH for a rapid saliva test that can be used to diagnose COVID-19.
STEM Translational Communication Center researchers have been awarded NIH grant which is testing the efficacy of using virtual technology to increase colorectal cancer screening among rural and minority patients.
When COVID-19 brought the tourism industry to a crashing halt this spring, farmers around the state quickly pivoted to sell the bounty of fruit and vegetables that were at peak harvest.
UF researchers Chang-Yu Wu, an engineer, and John Lednicky, a virologist, teamed up a decade ago to solve long-standing challenges in how air samples are collected and tested for viruses.
Dr. Balachandar answered questions on Reddit's Ask Science thread about how far infectious droplets could carry a virus in host-to-host transmission.
NIH has launched two adaptive clinical trials evaluating the safety and effectiveness of blood thinners to treat COVID-19.
The race to find effective treatments for COVID-19 isn’t just about developing new drugs. University of Florida Health scientists are studying a trio of existing medications known to have broad antiviral activity.
A protein thought to be the novel coronavirus’ entryway into the body could not be detected in the insulin-producing cells of the pancreas in three dozen individuals.