In January 2020, rumors of a nascent disease proliferating through Wuhan, China...
UF researchers respond to COVID-19
The latest UF research related to coronavirus
When the virus that causes COVID-19 enters the body, it hijacks cellular...
ntists can grow individual cell lines in a dish and study how the coronavirus infects them. And that’s useful as far as it goes. In a sense, however, it’s like studying how a car works by looking at just the carburetor. To gain the most insight, researchers want to study human lung tissue in its full, multidimensional glory, with all cell types represented.
people, however, soon discover the microscopic invader won’t allow them to return to their normal lives even months after infection. It’s an especially insidious side of the coronavirus that makes vaccination all the more important — COVID-19 as chronic illness.
The question kept coming up: Why are some countries in the grip of COVID-19 while others appear less affected?
It’s a pandemic seemingly without end. The latest coronavirus variant is fueling a surge in cases while Americans worry about ever-more infectious versions to come. The daily news is filled with talk of sickness, overburdened health care providers and the struggle to mask and vaccinate a nation. It’s a recipe for a mental health crisis.
A new study found that 35% of all COVID-19 infections are asymptomatic. Children are most likely to lack symptoms, while the elderly are least likely.
Convalescent plasma does not effectively prevent the progression of COVID-19 from a mild to severe form of the disease in high-risk patients, according to the results of a national clinical trial that involved University of Florida Health.
Meanwhile, an internal report by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention concluded the delta variant is as contagious as chickenpox and more transmissible than the viruses that cause seasonal flu, the common cold and Ebola.
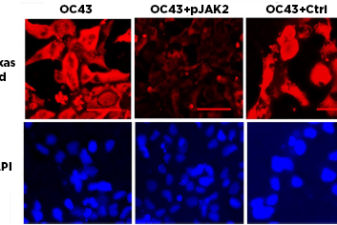
A team of UF researchers has identified dozens of novel therapeutic targets for the development of antiviral therapies against COVID-19 and other coronaviruses that infect people.
Patients with severe COVID-19 twice as likely to require future hospitalizations for other illnesses
People who have recovered from a bout of severe COVID-19 may still have reason for concern about their health.
A look back at the contributions of UF’s Emerging Pathogens Institute to campus-wide COVID-19 research.
University of Florida Health researchers are joining an ambitious global effort led by The Rockefeller Foundation to better track the coronavirus and its variants and set up a network of collaborators to stop any nascent pandemic in the future.
University of Florida Health researchers are joining an ambitious global effort led by The Rockefeller Foundation to better track the coronavirus and its variants and set up a network of collaborators to stop any nascent pandemic in the future.
Superfast, portable COVID-19 testing method detects the virus much faster than currently available methods.
An editorial by UF professors, published in the American Journal of Public Health, casts a spotlight on the plight of guest agricultural workers during the pandemic.
Despite pandemic complications, 30% of travelers would consider cruising next year, a survey from the University of Florida shows, with fans of cruising even more willing to get onboard.
The race to defeat the novel coronavirus took a major leap forward last week when the Food and Drug Administration and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention authorized the use of the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine in children 12 to 15 years old.
Small-scale grower operations have their advantages despite being challenged by access to large markets and limits on resources. In urban and rural environments, challenges that emerged from COVID-19 brought small-scale farms to light.
Recent work contributed to by UF mathematician Burton Singer seeks to estimate how COVID-19 vaccination campaigns will affect the future trajectory of the pandemic in the US.
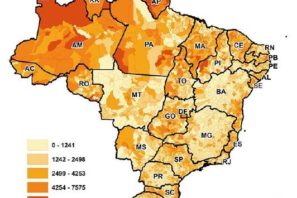
New research published in Science looks back at how COVID-19 spread over time throughout Brazil, to create a pandemic hotspot.
In recent years, public health emergencies caused by epidemics have led to the use of genome sequencing to identify and characterize viral pathogens.
The COVID-19 pandemic has been a lifesaver for shelter animals. During the...
It’s a term we’re going to hear much more frequently during the final chapter of the COVID-19 pandemic — herd immunity.
Imagine discovering an animal species you thought had gone extinct was still living – without laying eyes on it. Such was the case with the Brazilian frog species Megaelosia bocainensis.
UF investigators participate in the first study to determine that the CoronaVac vaccine is 50% effective at preventing COVID-19 in Manaus, Brazil where the P.1 variant is widespread.
Families are beginning to ask more questions about when COVID-19 vaccines will...
The UF Health lung transplant team has collaborated with researchers around the world to identify preliminary guidelines for successful transplantation in patients whose lungs have been permanently damaged by the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
Radio Hofstra University interviewed Dr. Amanda Phalin, a lecturer in the UF Warrington College of Business Management Department, about how the COVID-19 pandemic has impacted international trade. Check out Dr. Phalin’s insights in this radio interview.
The University of Florida will attempt to vaccinate more than 1,000 students as part of a landmark national study to determine whether young people who have received a COVID-19 vaccine can still spread the coronavirus.
Additional Stories
UF experts in the news